What is a MAP sensor
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor is a crucial component in modern vehicle engines, responsible for monitoring the air pressure within the intake manifold. This information is then used by the engine's electronic control unit (ECU) to optimize fuel delivery and ignition timing, ultimately improving engine performance and fuel efficiency.
The MAP sensor is typically located on the intake manifold, often near the throttle body or the cylinder head. Its strategic placement allows it to accurately measure the pressure changes that occur as air flows into the engine. By providing the ECU with real-time data on manifold pressure, the MAP sensor enables the engine management system to make necessary adjustments to the air-fuel mixture and ignition timing, ensuring optimal engine operation under various driving conditions.
Proper functioning of the MAP sensor is essential for maintaining the engine's efficiency and preventing issues such as poor acceleration, reduced fuel economy, and even engine damage. Regular inspection and timely replacement of a faulty MAP sensor are crucial for maintaining the overall health and performance of your vehicle's engine.
 MAP sensor
MAP sensor
Map sensor function
Map sensors play a critical role in modern vehicle systems, providing essential data that enables efficient engine performance and emissions control. Understanding the function of these sensors is key for maintaining optimal vehicle operation.
At the core of the map sensor's purpose is measuring the pressure within the intake manifold. This manifold pressure data is then used by the vehicle's electronic control unit (ECU) to determine the appropriate fuel delivery and ignition timing. By monitoring changes in manifold pressure, the ECU can make real-time adjustments to ensure the engine is operating at peak efficiency while minimizing harmful emissions.
Proper map sensor function is vital for maintaining driveability, fuel economy, and environmental compliance.
ALSO SEE: How to Test Ignition Coil with Multimeter
How does a MAP sensor work?
The MAP sensor works based on the piezoelectric effect. When the air pressure inside the intake manifold changes, the piezoelectric ceramic element inside the MAP sensor will deform, and this deformation is proportional to the size of the pressure. At this time, the MAP sensor will convert the pressure signal inside the sensor into an electrical signal and send it to the ECU, which will calculate the absolute pressure in the intake manifold according to the electrical signal sent by the MAP sensor, and adjust the engine fuel injection amount and ignition timing and other parameters according to this value.
Map sensor code
MAP sensor trouble codes can vary depending on the specific make and model of the vehicle, as well as the manufacturer's diagnostic trouble code (DTC) system. However, here are some common diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to MAP sensor issues that you may encounter:
1. P0105: MAP Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- This code indicates a problem with the MAP sensor circuit, such as a wiring issue or a faulty sensor.
2. P0106: MAP/BARO Sensor Range/Performance Problem
- This DTC suggests that the MAP sensor is reading values outside the expected range, which could be caused by a sensor calibration issue or a vacuum leak.
3. P0107: Manifold Absolute Pressure/Barometric Pressure Circuit Low Input
- This code indicates that the voltage from the MAP sensor is below the expected range, potentially due to a wiring fault or a faulty sensor.
4. P0108: Manifold Absolute Pressure/Barometric Pressure Circuit High Input
- This DTC signals that the voltage from the MAP sensor is higher than expected, which may be caused by a wiring problem or a malfunctioning sensor.
5. P0109: Manifold Absolute Pressure/Barometric Pressure Circuit Intermittent
- This code indicates intermittent issues with the MAP sensor circuit, which could be due to loose connections or sensor malfunctions that occur sporadically.
If you suspect an issue with your MAP sensor, it is recommended to use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the specific trouble code and diagnose the problem accurately.
What are the symptoms of a faulty MAP sensor?
Check Engine Light: One of the most common signs of a faulty MAP sensor is the illumination of the Check Engine Light on the dashboard. The onboard diagnostic system may detect issues with the MAP sensor and trigger a diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
Poor Engine Performance: A faulty MAP sensor can lead to poor engine performance, including rough idling, stalling, hesitation, or surging while driving. The engine may also feel underpowered or have difficulty accelerating smoothly.
Decreased Fuel Efficiency: A malfunctioning MAP sensor can disrupt the air-fuel ratio in the engine, leading to decreased fuel efficiency. You may notice a drop in fuel economy and increased fuel consumption.
Engine Misfires: Incorrect readings from the MAP sensor can result in improper fuel injection timing, leading to engine misfires. Misfires can cause vibrations, rough running, and potential damage to the engine over time.
Black Smoke from Exhaust: If the MAP sensor is sending incorrect signals to the engine control unit, it can cause the engine to run rich (too much fuel), resulting in black smoke coming from the exhaust.
Difficulty Starting the Engine: A faulty MAP sensor can cause starting issues, such as extended cranking times or difficulty starting the engine, especially when cold.
High Idle Speed: In some cases, a faulty MAP sensor can cause the engine to idle at a higher speed than normal, even when the vehicle is stationary.
How it affects your driving experience
A faulty MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure) sensor can greatly affect your driving experience by causing reduced engine performance, increased fuel consumption, engine stalling and surging, rough idling and vibrations, triggering the Check Engine Light, and leading to difficulty starting the engine. The improper readings from a malfunctioning MAP sensor can result in sluggish acceleration, hesitation, and lack of power, making driving less smooth and responsive. This can also impact fuel efficiency, leading to higher fuel costs and more frequent trips to the gas station. Engine stalling, unexpected surges, rough idling, and vibrations can create safety concerns and discomfort while driving. Additionally, the Check Engine Light may illuminate, signaling the need for attention. Addressing these issues promptly is crucial to ensure a safe, reliable, and enjoyable driving experience.
Diagnosing and Replacing a Faulty Map Sensor
Diagnosing and replacing a faulty MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure) sensor is essential to ensure proper engine performance and efficiency. By following the following steps to diagnose and replace a faulty MAP sensor, you can restore your vehicle's engine performance, fuel efficiency, and overall driving experience.Here are the steps involved in diagnosing and replacing a faulty MAP sensor:
1. Diagnostic Steps:
a. Check Engine Light: If the Check Engine Light is illuminated, use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the specific trouble code related to the MAP sensor.
b. Visual Inspection: Inspect the MAP sensor and its wiring harness for any visible damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
c. Testing the Sensor: Use a multimeter to test the sensor's voltage output while the engine is running to ensure it is within the specified range.
d. Vacuum Test: Perform a vacuum test to check if the sensor responds to changes in manifold pressure accurately.
e. Consult Service Manual: Refer to the vehicle's service manual for specific diagnostic procedures and specifications.
2. Replacement Steps:
a. Locate the MAP Sensor: Identify the location of the MAP sensor on the intake manifold or near the throttle body.
b. Disconnect Battery: Disconnect the vehicle's battery to prevent electrical shock and ensure safety during the replacement process.
c. Remove the Old Sensor: Unplug the electrical connector and remove the mounting screws holding the sensor in place.
d. Install the New Sensor: Install the new MAP sensor in the correct position, ensuring a secure fit and proper alignment.
e. Connect Wiring: Reconnect the electrical connector and secure it properly to ensure a reliable connection.
f. Reconnect Battery: Reconnect the vehicle's battery and clear any stored trouble codes using the OBD-II scanner.
g. Test Drive: Start the engine and test drive the vehicle to ensure the new MAP sensor functions correctly and resolves the initial symptoms.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Map Sensor
1. Regular Inspection: Check for damage and clean air filter.
2. Vacuum Lines: Ensure no leaks or blockages.
3. Quality Fuel: Use clean fuel to prevent buildup.
4. Maintenance Schedule: Follow manufacturer's recommendations.
5. Gentle Driving: Avoid harsh acceleration and braking.
6. Protect Sensor: Shield from dirt, oil, and moisture.
7. OEM Parts: Use quality parts for replacements.
8. Monitor Performance: Watch for changes and address issues promptly.
Map sensor vs Maf sensor
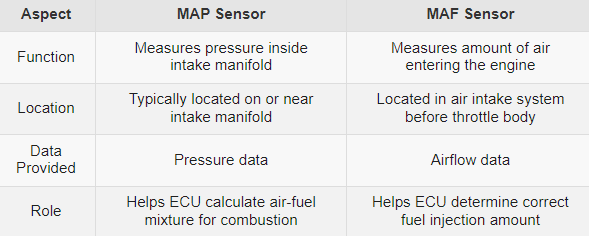
In summary, the MAP sensor measures pressure in the intake manifold, while the MAF sensor measures airflow entering the engine. Both sensors play crucial roles in the engine management system, providing essential data for the ECU to adjust fuel delivery and optimize engine performance.
Related topic: Mass Air Flow Sensor (MAF): What It is, Replacement & Working








