Transistors are fundamental electronic components that play a crucial role in modern electronics. NPN and PNP transistors are two common types used in various applications, including sensors and amplifiers. Understanding their symbols and working principles is essential for anyone working with electronic circuits. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the differences between NPN and PNP transistors, focusing on NPN sensors and PNP proximity sensors. We'll also address some frequently asked questions to clarify any doubts.
NPN vs PNP Transistors Featured Image
NPN Transistor
Symbol
The symbol for an NPN transistor consists of three layers: an arrow pointing away from the base (B) and towards the emitter (E), with the collector (C) in between. This symbol represents the flow of current when the transistor is in active mode.
Working Principle
- Emitter-Base Junction (EB Junction):When a small current flows from the emitter to the base (IB), it creates a larger current flow from the collector to the emitter (IC). This amplification of current is a key characteristic of NPN transistors.
- Operation Modes:NPN transistors can operate in two modes: ON (active) and OFF (cut-off). In the ON state, the transistor allows current to flow from collector to emitter. In the OFF state, there is no current flow.
- Common Applications:NPN transistors are widely used in amplification circuits, switching applications, and NPN sensors, where their ability to provide a low signal when active is advantageous.

NPN Transistor
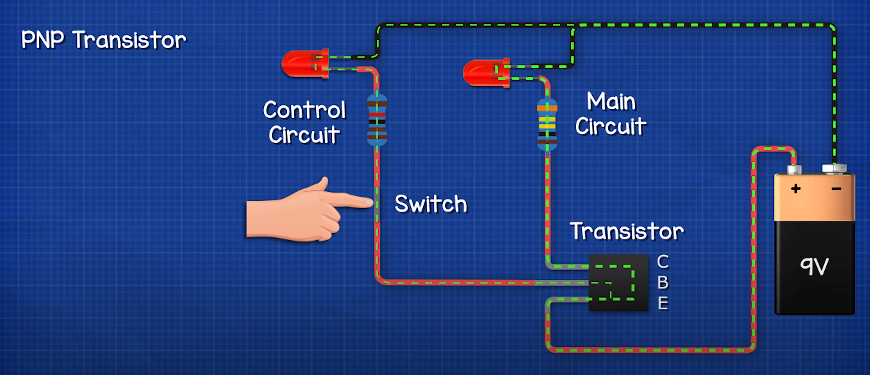
PNP Transistor
Symbol
The symbol for a PNP transistor also consists of three layers: an arrow pointing towards the base (B) and away from the emitter (E), with the collector (C) in between. This symbol represents the flow of current when the transistor is in active mode.
PNP Transistor
Working Principle
- Emitter-Base Junction (EB Junction):Similar to NPN transistors, a small current flowing from the emitter to the base (IB) in PNP transistors results in a larger current from the collector to the emitter (IC).
- Operation Modes:PNP transistors also operate in two modes: ON (active) and OFF (cut-off). In the ON state, the transistor allows current to flow from emitter to collector. In the OFF state, there is no current flow.
- Common Applications:PNP transistors are frequently used in amplification circuits, switching applications, and PNP proximity sensors, where their ability to provide a high signal when active is beneficial.
The Role of Power Lines in Electronic Systems
Power lines are the arteries of electrical systems, delivering electricity from generators to homes, businesses, and industries. Ensuring the reliable and efficient transmission of electrical power is a critical consideration in electronics and electrical engineering. Power lines carry various voltages, and transformers are essential in maintaining the appropriate voltage levels throughout the distribution network.
NPN Sensor vs. PNP Proximity Sensor
NPN Sensor
NPN sensors are commonly used in applications where the output is connected to the ground (0V). These sensors provide a low signal when active. For example, in an NPN sensor, when an object is detected, it connects the output to ground, creating a path for current to flow.
PNP Proximity Sensor
On the other hand, PNP proximity sensors are used in applications where the output is connected to the positive power supply. These sensors provide a high signal when active. When an object is detected, a connection to the positive supply voltage is established, allowing current to flow.
Key Differences Between NPN and PNP Sensors
- Output Signal Polarity:The primary difference between NPN and PNP sensors is the polarity of their output signals. NPN sensors provide a low signal (0V) when active, while PNP sensors provide a high signal (positive supply voltage) when active.
- Wiring Configuration:NPN sensors are typically wired with the output connected to ground, making them suitable for sinking current. In contrast, PNP sensors are wired with the output connected to the positive supply voltage, making them suitable for sourcing current.
- Compatibility:When selecting sensors for a specific application, it's crucial to consider the compatibility with the rest of the circuit. The choice between NPN and PNP sensors depends on the existing circuit configuration and requirements.
Final Verdict
In summary, NPN and PNP transistors have distinct symbols and current flow directions, making them suitable for different applications. NPN sensors provide a low signal when active and are grounded, while PNP proximity sensors offer a high signal and connect to the positive power supply. Understanding these differences is essential for designing electronic circuits effectively. For more in-depth knowledge, visit jak electronics for additional resources and guidance.






